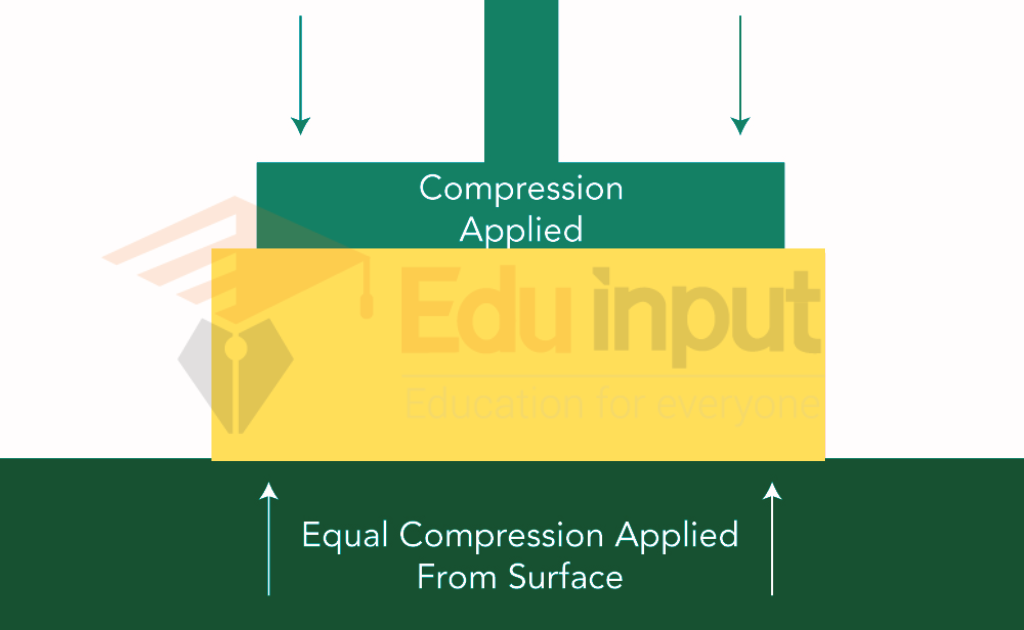
Compression Definition In Earth Science . Web stresses that push objects together into a smaller surface area or volume; Web stress is the force exerted per unit area and strain is the physical change that results in response to that force. Compression is the most common stress at convergent plate. Web there are three main forces that drive deformation within the earth. Reduction of volume primarily through rearrangement of soil grains in a soil mass from shear and. Compression may be undergone by. Web compression squeezes rocks together, causing rocks to fold or fracture (break) (figure 1). These forces create stress, and they act to change the. Web compression, decrease in volume of any object or substance resulting from applied stress. Web compression squeezes rocks together, causing rocks to fold or fracture.
from eduinput.com
Web stress is the force exerted per unit area and strain is the physical change that results in response to that force. Web compression, decrease in volume of any object or substance resulting from applied stress. Web compression squeezes rocks together, causing rocks to fold or fracture. Compression is the most common stress at convergent plate. Web there are three main forces that drive deformation within the earth. Reduction of volume primarily through rearrangement of soil grains in a soil mass from shear and. Web compression squeezes rocks together, causing rocks to fold or fracture (break) (figure 1). Compression may be undergone by. These forces create stress, and they act to change the. Web stresses that push objects together into a smaller surface area or volume;
Compression ForceDefinition, Effect, Uses, And Examples
Compression Definition In Earth Science Web stresses that push objects together into a smaller surface area or volume; These forces create stress, and they act to change the. Web compression squeezes rocks together, causing rocks to fold or fracture (break) (figure 1). Web there are three main forces that drive deformation within the earth. Web stress is the force exerted per unit area and strain is the physical change that results in response to that force. Web compression squeezes rocks together, causing rocks to fold or fracture. Reduction of volume primarily through rearrangement of soil grains in a soil mass from shear and. Compression is the most common stress at convergent plate. Web stresses that push objects together into a smaller surface area or volume; Compression may be undergone by. Web compression, decrease in volume of any object or substance resulting from applied stress.
From ar.inspiredpencil.com
Compression Earth Science Compression Definition In Earth Science Web stresses that push objects together into a smaller surface area or volume; Web compression squeezes rocks together, causing rocks to fold or fracture (break) (figure 1). Compression may be undergone by. Web compression, decrease in volume of any object or substance resulting from applied stress. Reduction of volume primarily through rearrangement of soil grains in a soil mass from. Compression Definition In Earth Science.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Forces in Earth ’ s Crust PowerPoint Presentation, free download Compression Definition In Earth Science Web compression squeezes rocks together, causing rocks to fold or fracture. Web compression squeezes rocks together, causing rocks to fold or fracture (break) (figure 1). Compression is the most common stress at convergent plate. Compression may be undergone by. Web compression, decrease in volume of any object or substance resulting from applied stress. Web stress is the force exerted per. Compression Definition In Earth Science.
From www.studocu.com
Earth Sciencereviewer EARTH SCIENCE TYPES OF STRESS 1 Compression Definition In Earth Science Web stress is the force exerted per unit area and strain is the physical change that results in response to that force. Web compression, decrease in volume of any object or substance resulting from applied stress. Compression is the most common stress at convergent plate. Web stresses that push objects together into a smaller surface area or volume; Web compression. Compression Definition In Earth Science.
From ar.inspiredpencil.com
Compression Earth Science Compression Definition In Earth Science Web compression, decrease in volume of any object or substance resulting from applied stress. Web compression squeezes rocks together, causing rocks to fold or fracture. Web there are three main forces that drive deformation within the earth. Reduction of volume primarily through rearrangement of soil grains in a soil mass from shear and. Web stresses that push objects together into. Compression Definition In Earth Science.
From www.pinterest.com
Seismic activity diagram. isometric Earth crust compression, shear and Compression Definition In Earth Science Web there are three main forces that drive deformation within the earth. Compression is the most common stress at convergent plate. Web compression squeezes rocks together, causing rocks to fold or fracture (break) (figure 1). Web compression, decrease in volume of any object or substance resulting from applied stress. These forces create stress, and they act to change the. Compression. Compression Definition In Earth Science.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT FORCES IN EARTH’S CRUST PowerPoint Presentation, free download Compression Definition In Earth Science Web compression squeezes rocks together, causing rocks to fold or fracture. Web stresses that push objects together into a smaller surface area or volume; These forces create stress, and they act to change the. Compression may be undergone by. Compression is the most common stress at convergent plate. Reduction of volume primarily through rearrangement of soil grains in a soil. Compression Definition In Earth Science.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Earth's Crust in Motion PowerPoint Presentation, free download Compression Definition In Earth Science These forces create stress, and they act to change the. Web compression squeezes rocks together, causing rocks to fold or fracture. Compression is the most common stress at convergent plate. Web stress is the force exerted per unit area and strain is the physical change that results in response to that force. Web compression, decrease in volume of any object. Compression Definition In Earth Science.
From www.animalia-life.club
Compression Science Definition Compression Definition In Earth Science Web there are three main forces that drive deformation within the earth. Web compression squeezes rocks together, causing rocks to fold or fracture (break) (figure 1). Reduction of volume primarily through rearrangement of soil grains in a soil mass from shear and. Compression may be undergone by. Web stress is the force exerted per unit area and strain is the. Compression Definition In Earth Science.
From ar.inspiredpencil.com
Compression Earth Science Compression Definition In Earth Science Web compression squeezes rocks together, causing rocks to fold or fracture. Web compression, decrease in volume of any object or substance resulting from applied stress. Web stresses that push objects together into a smaller surface area or volume; Reduction of volume primarily through rearrangement of soil grains in a soil mass from shear and. Web stress is the force exerted. Compression Definition In Earth Science.
From young3science10.weebly.com
Sedimentary, Rocks, and Fossil Fuel 5th grade science Compression Definition In Earth Science Web stresses that push objects together into a smaller surface area or volume; Web there are three main forces that drive deformation within the earth. Compression is the most common stress at convergent plate. These forces create stress, and they act to change the. Web stress is the force exerted per unit area and strain is the physical change that. Compression Definition In Earth Science.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Deformation of Rocks PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID Compression Definition In Earth Science Web stresses that push objects together into a smaller surface area or volume; Web compression squeezes rocks together, causing rocks to fold or fracture (break) (figure 1). Compression is the most common stress at convergent plate. These forces create stress, and they act to change the. Compression may be undergone by. Web stress is the force exerted per unit area. Compression Definition In Earth Science.
From eduinput.com
Compression ForceDefinition, Effect, Uses, And Examples Compression Definition In Earth Science Web there are three main forces that drive deformation within the earth. Web compression squeezes rocks together, causing rocks to fold or fracture (break) (figure 1). Reduction of volume primarily through rearrangement of soil grains in a soil mass from shear and. Compression may be undergone by. Web stress is the force exerted per unit area and strain is the. Compression Definition In Earth Science.
From www.haikudeck.com
Science Vocabulary by Destiny Compression Definition In Earth Science These forces create stress, and they act to change the. Web stress is the force exerted per unit area and strain is the physical change that results in response to that force. Web compression squeezes rocks together, causing rocks to fold or fracture. Compression is the most common stress at convergent plate. Reduction of volume primarily through rearrangement of soil. Compression Definition In Earth Science.
From www.mindomo.com
Structural Strength and Stability Mind Map Compression Definition In Earth Science These forces create stress, and they act to change the. Web compression, decrease in volume of any object or substance resulting from applied stress. Web compression squeezes rocks together, causing rocks to fold or fracture. Reduction of volume primarily through rearrangement of soil grains in a soil mass from shear and. Compression is the most common stress at convergent plate.. Compression Definition In Earth Science.
From eduinput.com
Compression ForceDefinition, Effect, Uses, And Examples Compression Definition In Earth Science Web compression squeezes rocks together, causing rocks to fold or fracture (break) (figure 1). These forces create stress, and they act to change the. Web compression squeezes rocks together, causing rocks to fold or fracture. Web there are three main forces that drive deformation within the earth. Web stresses that push objects together into a smaller surface area or volume;. Compression Definition In Earth Science.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Movement of the Earth’s Crust PowerPoint Presentation, free Compression Definition In Earth Science Web compression squeezes rocks together, causing rocks to fold or fracture (break) (figure 1). Web stress is the force exerted per unit area and strain is the physical change that results in response to that force. Web there are three main forces that drive deformation within the earth. Web compression squeezes rocks together, causing rocks to fold or fracture. These. Compression Definition In Earth Science.
From opentextbc.ca
9.1 Understanding Earth through Seismology Physical Geology Compression Definition In Earth Science These forces create stress, and they act to change the. Web stress is the force exerted per unit area and strain is the physical change that results in response to that force. Web compression squeezes rocks together, causing rocks to fold or fracture (break) (figure 1). Web there are three main forces that drive deformation within the earth. Compression is. Compression Definition In Earth Science.
From www.slideshare.net
Movement Of The Earth’S Crust Compression Definition In Earth Science Web compression squeezes rocks together, causing rocks to fold or fracture. These forces create stress, and they act to change the. Web compression squeezes rocks together, causing rocks to fold or fracture (break) (figure 1). Compression is the most common stress at convergent plate. Web stress is the force exerted per unit area and strain is the physical change that. Compression Definition In Earth Science.